TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry:
- Basics of Air Handlers explains what air handlers are, how they work in your HVAC system, and why they matter for airflow and comfort.
- Learn how air handlers move conditioned air through your home, support your heating and cooling equipment, and impact indoor air quality.
- The guide breaks down key components like blowers, coils, and filters so you understand how each part contributes to performance.
- Use this info to better maintain your system, improve efficiency, and make informed HVAC decisions.
An air handler, often referred to as an HVAC air handler, is a crucial part of the heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) system. It is responsible for circulating air throughout your home or business, ensuring that your indoor spaces remain comfortable and well-ventilated. The air handler works in conjunction with your air conditioning system or heat pump to regulate temperature and humidity, providing a stable and pleasant environment. Understanding the Basics of Air Handlers helps homeowners and business owners maintain optimal performance and energy efficiency in their HVAC systems.
Table of Contents
How Air Handlers Support Comfort and Efficiency in HVAC Systems
The Role of Air Handlers in HVAC Systems
Air handlers serve as the lungs of your HVAC system. By efficiently moving air throughout your space, they ensure that every corner of your home or office receives the right amount of conditioned air. This not only maintains comfort but also helps in evenly distributing air, minimizing hot or cold spots.
Types of Air Handlers
Air handlers come in various configurations, catering to different needs. Some are designed for residential use, offering compact designs that fit into smaller spaces, while others are built for commercial purposes, providing higher capacity and more robust construction. Choosing the right type depends on factors such as the size of your space, the existing HVAC system, and specific climate control needs.

Importance of Proper Installation
Proper installation of air handlers is critical to their performance. An improperly installed unit can lead to inefficiencies, higher energy consumption, and increased wear and tear. It’s essential to work with experienced professionals who understand the intricacies of HVAC systems and can ensure that your air handler is installed correctly for optimal performance.
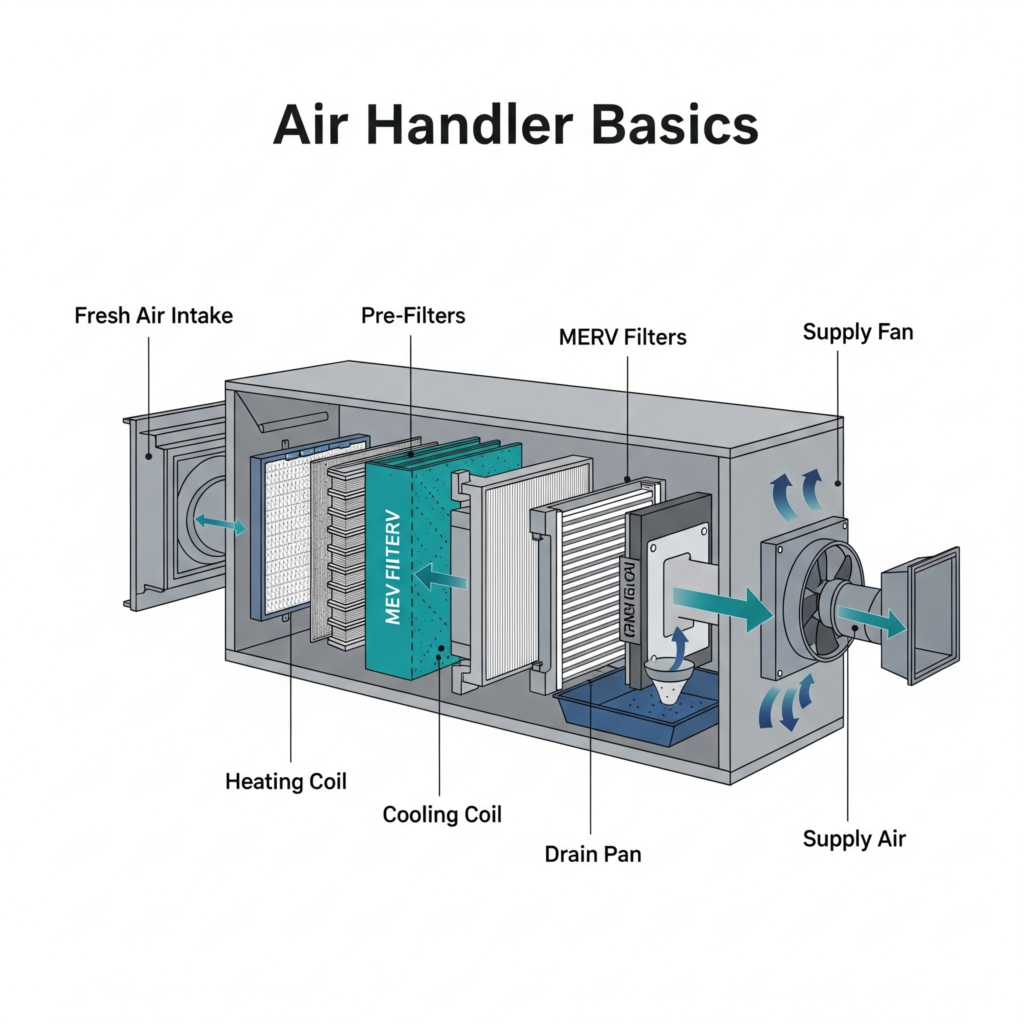
Components of an Air Handler
An air handler unit is composed of several key components that work together to move and condition the air. These include:
Blower
The blower is the component that moves air through the ductwork in your home. It can be either a single-speed or variable-speed motor, impacting how efficiently and quietly it operates. A variable-speed blower can adjust its speed based on the heating or cooling demand, providing better temperature control and energy efficiency.
Coils
The coils, typically made of copper or aluminum, are where heat exchange occurs. In air conditioning mode, refrigerant circulates through the coils to absorb heat and cool the air. The quality and condition of these coils are crucial, as they directly affect the efficiency and performance of the air handler. Regular cleaning and maintenance can prevent issues like ice buildup or reduced airflow.
Filters
Air filters trap dust, pollen, and other airborne particles, improving indoor air quality. It’s important to replace these regularly to maintain efficiency. High-efficiency filters can capture smaller particles, offering better protection against allergens and pollutants. However, it’s important to balance filtration with airflow to prevent strain on the system.
Dampers
These regulate airflow within the system, ensuring balanced distribution throughout your home. Dampers can be manually adjusted or automatically controlled, depending on the complexity of your HVAC system. Properly functioning dampers help maintain consistent temperatures and reduce energy waste by directing air where it’s needed most.
Control Systems
These include thermostats and other devices that manage the operation of the air handler and overall HVAC system. Advanced control systems offer programmable settings, allowing you to tailor your HVAC operation to your lifestyle and schedule, further enhancing comfort and efficiency. Smart thermostats can even learn your preferences over time, optimizing performance with minimal input.
Where is the Air Handler Located?

The air handler is typically located indoors, often in a utility closet, attic, or basement. In residential settings, you might find it near the furnace or central air conditioning unit. In commercial properties, air handlers can be larger and may be located in dedicated mechanical rooms. Knowing where your air handler is situated can help you quickly address any issues that arise and facilitate regular maintenance.
Residential Installations
In residential properties, air handlers are often placed in spaces that are easily accessible for maintenance, such as utility closets or basements. These locations are chosen for their proximity to ductwork and ease of access for routine service, making it convenient to perform regular checks and maintenance without disrupting your daily activities.
Commercial Installations
In commercial settings, air handlers might be located in more centralized mechanical rooms. These rooms are designed to house larger units needed to service bigger spaces, ensuring that air conditioning and heating are distributed effectively throughout the property. The placement is often strategic to minimize noise and vibration in work areas while allowing for easy access for maintenance.
Factors Influencing Location
The location of an air handler can be influenced by several factors, including building design, space constraints, and HVAC system configuration. Proper placement is crucial for optimal performance and efficiency, as it affects air distribution and the ease of conducting maintenance and repairs. Consulting with HVAC professionals can help determine the best location for your air handler based on your specific needs and building layout.
How Does an Air Handler Work?
The operation of an air handler is relatively straightforward. When your thermostat signals a need for heating or cooling, the air handler kicks into action. Here’s a step-by-step look at how it functions:
Air Intake
The air handler draws in air from the interior of the building. This process begins when the thermostat detects a temperature change and sends a signal to the air handler. The intake process is crucial as it sets the stage for filtration and conditioning, ensuring that the air moving through the system is clean and fresh.
Filtration
The air passes through filters to remove dust and other particles. Effective filtration is essential for maintaining indoor air quality and protecting the air handler’s components from dust and debris. Regular filter changes are necessary to keep the system running smoothly and to prevent blockages that can hinder airflow and efficiency.
Conditioning
Depending on the season, the air is either heated or cooled as it passes over the coils. This step involves heat exchange, where refrigerant absorbs or releases heat, altering the air’s temperature to meet your comfort needs. The efficiency of this process is dependent on the condition of the coils and the refrigerant levels, which should be checked regularly.
Distribution
The conditioned air is then circulated back into the building through the ductwork, maintaining a consistent indoor climate. This distribution is managed by the blower and dampers, ensuring that air reaches every part of the building evenly. Proper distribution is key to maintaining comfort, preventing hot or cold spots, and optimizing energy use.
Cycle Efficiency
This process repeats as needed, ensuring your home remains comfortable year-round. The efficiency of this cycle is greatly influenced by the quality of the air handler and the regularity of maintenance. Regular inspections and maintenance can prevent issues like airflow obstructions or mechanical failures, ensuring that your system operates at peak efficiency.
Why Are Air Handlers Important?
Air handlers play a vital role in maintaining indoor air quality and comfort. They are integral to the HVAC system’s ability to efficiently regulate temperature and humidity, which can impact everything from energy bills to health. Reliable air handlers help:
Improve Air Quality
By filtering out pollutants and allergens, air handlers contribute to healthier indoor environments. Poor air quality can lead to health issues such as allergies and respiratory problems, making effective filtration a top priority for maintaining a healthy living or working space.
Enhance Efficiency
A well-functioning air handler ensures your HVAC system operates efficiently, reducing energy consumption and costs. Efficient air handlers help lower utility bills by minimizing waste and optimizing the use of energy, providing a significant return on investment over time.
Extend Equipment Life
Regular maintenance of air handlers can prevent breakdowns and prolong the lifespan of your HVAC system. By addressing minor issues before they escalate, you can avoid costly repairs and extend the service life of your equipment, ensuring reliable performance for years to come.
Support Comfortable Living
Beyond technical benefits, air handlers directly influence your comfort. A consistent climate, free from extreme temperature variations, enhances the overall living or working experience, making your home or business a more pleasant place to be.
Choosing the Right Air Handler
Selecting the appropriate air handler for your home or business is essential. Factors to consider include:
Size Considerations
The air handler must be appropriately sized to match your HVAC system and the square footage of your space. An undersized unit may struggle to meet demand, while an oversized one can lead to inefficiencies and increased wear and tear. Professional assessment can help determine the right size for your needs.
Efficiency Features
Look for models with variable-speed motors and energy-efficient features to maximize performance and minimize costs. Advanced technologies, such as smart controls and high-efficiency coils, can enhance the air handler’s effectiveness, offering better comfort and lower energy bills.
System Compatibility
Ensure the air handler is compatible with your existing system, whether it’s a heat pump, central air conditioner, or furnace. Compatibility is crucial for seamless operation and can prevent issues related to mismatched components, such as poor performance or increased energy use.
Professional Guidance
At BOOST SERVICES, we provide tailored solutions to meet your specific needs, ensuring you receive the most suitable air handler for your property. Our team of experts can guide you through the selection process, helping you choose a unit that aligns with your requirements and budget.
Maintenance Tips for Air Handlers
Regular maintenance is key to keeping your air handler and HVAC system in optimal condition. Here are some tips to consider:

Change Filters Regularly
Replace air filters every 1-3 months, or as recommended by the manufacturer, to maintain airflow and efficiency. Keeping filters clean is one of the simplest yet most effective ways to ensure your system runs smoothly and prevents unnecessary strain on the components.
Inspect Coils and Blower
Ensure coils are clean and free of debris, and check the blower for any signs of wear or damage. Regular inspections can catch issues early, such as coil blockages or blower malfunctions, allowing for timely repairs that prevent further damage and maintain performance.
Schedule Professional Tune-Ups
Regular inspections and maintenance by HVAC professionals can catch issues early and ensure your system runs smoothly. Professional tune-ups include comprehensive checks of all components, adjustments, and cleaning, helping to extend the life of your air handler and improve its efficiency.
Monitor System Performance
Pay attention to any changes in your system’s performance, such as unusual noises or temperature fluctuations. Early detection of anomalies can prevent major breakdowns and costly repairs, ensuring that your air handler continues to provide reliable comfort.
Conclusion
Understanding the basics of air handlers empowers you to make informed decisions about your HVAC system. Whether you’re a community-based entrepreneur seeking reliable HVAC solutions or a working-class American needing quick and efficient service, BOOST SERVICES is here to help. Our commitment to quality and customer satisfaction ensures you receive the best service possible.
For expert assistance with your HVAC needs, contact BOOST SERVICES today at 818-277-5056 or 747-264-6358. Let us help you maintain a comfortable and efficient home or business environment.
Basics of Air Handlers gives a clear overview of air handler function and parts. Understanding them helps you optimize comfort, circulation, and HVAC operation in your home.
FAQ:
What is an air handler and what does it do?
An air handler is a central component of your HVAC system that regulates and circulates conditioned air (heated or cooled) throughout your home via ductwork. It works with your AC, heat pump, or furnace to maintain comfortable indoor temperatures.
What are the key parts inside an air handler?
Common components include the blower motor (pushes air through the system), evaporator coil (conditions the air), and air filter (removes particles like dust and pollen), all working together for effective airflow.
How does an air handler impact indoor air quality?
The air filter inside the air handler traps dust, allergens, and debris, helping improve indoor air quality while protecting internal components from clogging or damage.
Where is an air handler usually located in a home?
Air handlers are typically installed indoors — in areas like the attic, basement, garage, or utility closet — to connect easily to ductwork and other HVAC components.
How often should I maintain or replace parts of my air handler?
Filters should be checked and replaced regularly (often every 1–3 months), and routine professional maintenance helps prevent issues, improve efficiency, and extend the unit’s lifespan.
What are some signs my air handler needs service?
Common signs include weak airflow, strange noises, uneven temperatures, or higher energy bills — all of which can indicate issues with the blower, coils, or airflow.

